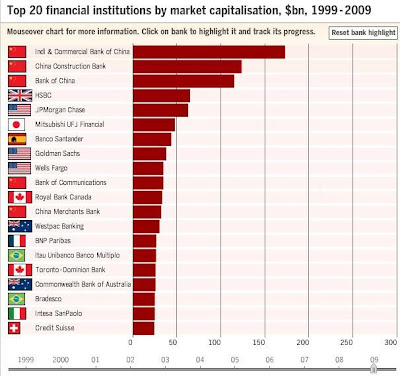
 Now we can fast forward to 2009 and a completely different picture emerges.
Now we can fast forward to 2009 and a completely different picture emerges. China now holds the top 3 spots and America’s largest bank, JP Morgan Chase is merely in 5th place. You can do a whole range of further comparisons but the overwhelming conclusion must be that the financial world today is far different from a decade ago. And the power players have clearly shifted. If power were to be measured by the strength of financial institutions, 2009 must be considered a much more egalitarian world. No longer could the fate of things to come be dictated by one superpower only. An interesting thought considering the upcoming G20 meeting.
"Also to be factored in is the amount of money being given out to companies by private equity," cautions Jacoline Loewen, author of Money Magnet. "A lot of the business done by banks is shifting to private equity which does not show up on these charts."

